Search K
Appearance
Appearance
IndexedDB是一个基于键值对的数据库,可以用来存储大量结构化数据。它可以用来缓存资源,以便在离线时使用。mdn介绍
对比localStorage,sessionStorage,cookie等存储方式 IndexedDB有以下优势:
| localStorage | sessionStorage | cookie | IndexedDB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效期 | 永久有效 | 关闭浏览器清除 | 非持久化,刷新页面则刷新 | 永久有效 |
| 存储容量 | 一般5MB | 一般5MB | 一般4KB | 无上限 |
| 存储类型限制 | 可JSON序列化的值 | 可JSON序列化的值 | 可JSON序列化的值 | 存储结构化克隆算法支持的任何对象 |
| 存取数据任务类型 | 同步 | 同步 | 同步 | 异步,同步 |
| 同域限制 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
基本上所有现代浏览器都支持IndexedDB 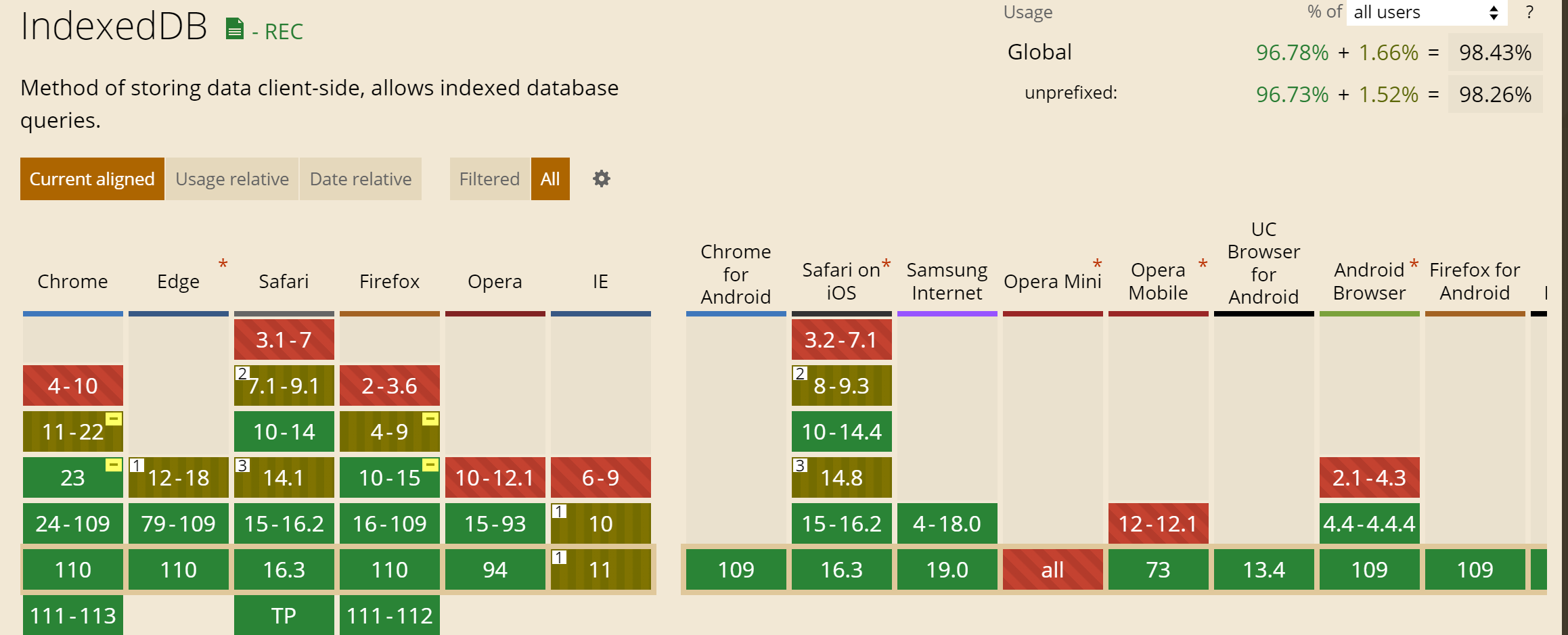
数据库是一个逻辑容器,用于存储数据。一个数据库可以包含多个对象存储空间(object store)。每个数据库都有一个名称,用于唯一标识它。
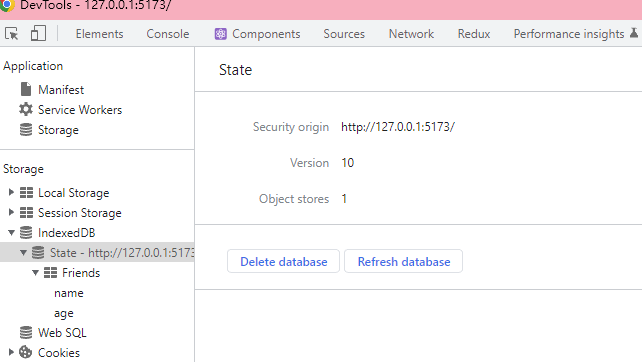
打开f12可以在Application中看到IndexedDB中的数据库, 也可以在浏览器的控制台中输入indexedDB查看
对象存储空间是一个逻辑容器,用于存储对象。对象存储空间中的对象都有一个键,用于唯一标识它们。对象存储空间中的对象都有一个键,用于唯一标识它们。
索引是一个逻辑容器,用于存储对象的键。索引允许你快速访问对象,而不用遍历整个对象存储空间。 key为model中声明的主键(如:Friends: '++id, name, age',),注意不要将文件,大字符串存储在索引中. 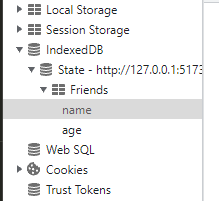
事务是一组操作的集合,这些操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
mdn备注:IndexedDB API 是强大的,但对于简单的情况可能看起来太复杂。如果你更喜欢一个简单的 API,请尝试 localForage、dexie.js、PouchDB、idb、idb-keyval、JsStore 或者 lovefield 之类的库,这些库使 IndexedDB 对开发者来说更加友好。 这里我们采用dexie.js进行开发
dexie.js是一个轻量级的IndexedDB封装库,它提供了一个简单的API来操作IndexedDB。dexie.js的API设计参考了jQuery的API设计,因此非常容易上手。
yarn
yarn add dexienpm
npm install dexie在src/models目录下创建State.ts文件
import Dexie, { Table } from 'dexie';
export interface Friend {
id?: number;
name: string;
age: number;
headImg: string;
}
export class State extends Dexie {
// friends 表类型声明
Friends!: Table<Friend>;
constructor() {
super('State');
// 若表结构改变需更改版本号
this.version(1).stores({
// 主键 id 自增, name,age作为索引 不要将文件,大字符串存储在索引中.如Friend.headImg
Friends: '++id, name, age',
});
}
}
export const { Friends } = new State();在src/controllers目录下创建State.ts文件
import { Friend, Friends } from "../models/State";
/**
* @description 查询
*/
export async function getFriend(id:string){
const friend = await Friends.get(id);
return friend;
}
/**
* @description 查询年龄为age的所有朋友
*/
export async function getFriendsByAge(age:number){
const friends = await Friends.where("age").equals(age).toArray();
return friends;
}
/**
* @description 获取所有朋友
*/
export async function getAllFriends(){
const friends = await Friends.toArray();
return friends;
}
/**
* @description 添加朋友
*/
export async function addFriend(data:Friend){
const id = await Friends.add(data);
return id;
}
/**
* @description 更新朋友
*/
export async function updateFriend(data:Friend){
const id = await Friends.put(data);
return id;
}
/**
* @description 删除朋友
*/
export async function deleteFriend(id:string){
return await Friends.delete(id);
}import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import mock from 'mockjs';
import './App.css';
import { Button, Table, TableProps } from 'antd';
import { Friend } from './models/State';
import { addFriend, getAllFriends } from './controllers/State';
import img1 from './img/缓存/1.jpg';
import img2 from './img/缓存/2.jpg';
const App: React.FC<AppProps> = () => {
const [dataSource, setDataSource] = useState<Friend[]>([]);
const columns = [
{
title: 'id',
dataIndex: 'id',
},
{
title: '姓名',
dataIndex: 'name',
},
{
title: '年龄',
dataIndex: 'age',
},
{
title: '头像',
dataIndex: 'headImg',
render: (text: string) => (
<img width={50} height={50} src={text} alt="" />
),
},
];
useEffect(() => {
request();
}, []);
async function request() {
const res = await getAllFriends();
setDataSource(res);
}
const tableConfig: TableProps<Friend> = {
columns,
dataSource,
rowKey: 'id',
};
return (
<div>
<Table {...tableConfig}></Table>
<Button
onClick={async () => {
const headImg = await imgToBase64(Math.random() > 0.5 ? img1 : img2);
const data = mock.mock({
name: '@cname',
age: '@integer(18, 60)',
headImg,
});
await addFriend(data);
await request();
}}>
添加随机朋友
</Button>
</div>
);
};
interface AppProps {}
export default App;
App.displayName = 'App';
async function imgToBase64(url: string) {
const res = await fetch(url, {});
const blob = await res.blob();
return await blobToBase64(blob);
}
function blobToBase64(blob: Blob): Promise<string> {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(blob);
return new Promise((resolve) => {
reader.onloadend = () => {
resolve(reader.result as string);
};
});
}<script setup lang="ts">
import {
addFriend,
getAllFriends,
} from './controllers/State';
import mock from 'mockjs';
import img1 from './img/缓存/1.jpg';
import img2 from './img/缓存/2.jpg';
import { Friend } from './models/State';
import { Button, Table, TableProps } from 'ant-design-vue';
import { h, reactive } from 'vue';
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/antd.css';
const dataSource = reactive<Friend[]>([]);
const columns = [
{
title: 'id',
dataIndex: 'id',
},
{
title: '姓名',
dataIndex: 'name',
},
{
title: '年龄',
dataIndex: 'age',
},
{
title: '头像',
dataIndex: 'headImg',
customRender: ({
text,
index,
}: {
text: string;
index: number;
}) => {
return h('img', { src: text, width: 50, height: 50 });
},
},
];
request();
async function add() {
const headImg = await imgToBase64(
Math.random() > 0.5 ? img1 : img2,
);
const data = mock.mock({
name: '@cname',
age: '@integer(18, 60)',
headImg,
});
await addFriend(data);
await request();
}
async function request() {
const res = await getAllFriends();
dataSource.splice(0, dataSource.length, ...res);
return res;
}
async function imgToBase64(url: string) {
const res = await fetch(url, {});
const blob = await res.blob();
return await blobToBase64(blob);
}
function blobToBase64(blob: Blob): Promise<string> {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(blob);
return new Promise((resolve) => {
reader.onloadend = () => {
resolve(reader.result as string);
};
});
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<Table
:data-source="dataSource"
:row-key="'id'"
:columns="columns"
/>
<Button @click="add">添加好友</Button>
</div>
</template>效果图 
每次点击添加按钮都会向数据库中添加一条数据,并且会重新渲染,存入数据库中的值是永久有效的。 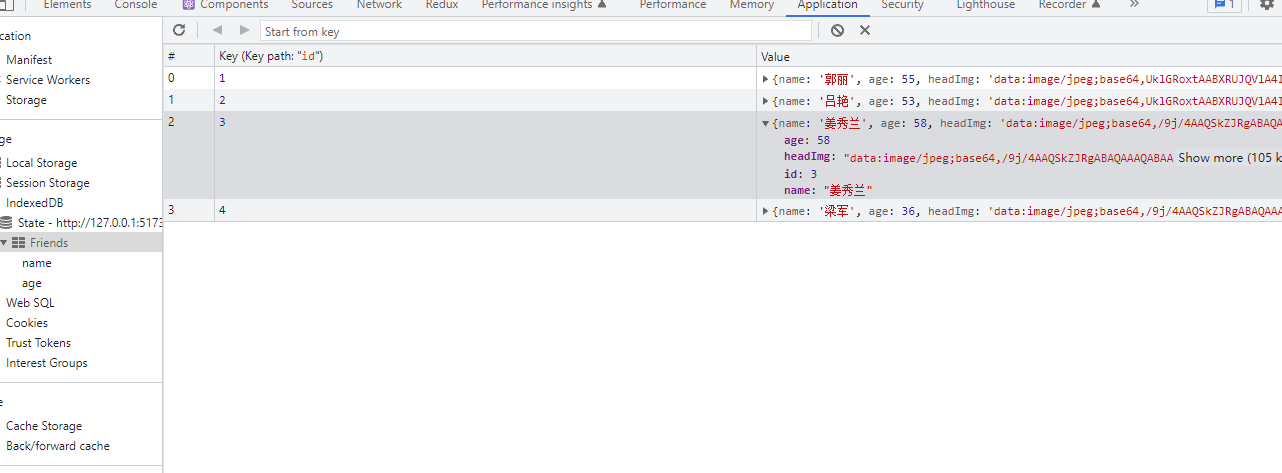
使用我们已经基本了解,那么我们就可以开始创建缓存工具类了,我们需要实现的功能有:
/src/models/Cache.ts
// db.ts
import Dexie, { Table } from 'dexie';
/** 资源缓存 */
export type ResourceCacheType = {
id?: number;
/** 资源路径 */
url: string;
/** 资源内容 */
content: Blob;
/** 资源最后修改时间 */
timestamp: number;
/** 过期时间 */
expireTime?: number;
};
// 若数据结构改变应当修改版本号
class Cache extends Dexie {
ResourceCache!: Table<ResourceCacheType>;
constructor() {
super('Cache');
this.version(1).stores({
// Primary key and indexed props 索引 不要索引文件
ResourceCache: '++id, url,timestamp',
});
}
}
export const { ResourceCache } = new Cache();/src/controllers/ResourceCache.ts
import { ResourceCache } from '../models/Cache';
export async function getCache(url: string) {
try {
return await ResourceCache.where('url')
.equals(url)
.first();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
}
export async function setCache(data: {
url: string;
content: Blob;
expireTime?: number;
}) {
try {
const cache = await getCache(data.url);
if (cache?.id) {
// 更新缓存
return await ResourceCache.update(cache.id, {
...data,
timestamp: Date.now(),
});
}
return await ResourceCache.add({
...data,
timestamp: Date.now(),
});
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
}
// 将所有过期的缓存清除
export async function clearCache() {
const caches = await ResourceCache.toArray();
caches.forEach((cache) => {
if (cache.expireTime) {
const now = Date.now();
const timestamp = cache.timestamp;
if (now - timestamp > cache.expireTime) {
ResourceCache.delete(cache.id!);
}
}
});
}/src/util/ResourceCache.ts
import {
clearCache,
getCache,
setCache,
} from '../controllers/ResourceCache';
/**
* @description 通用缓存策略
*/
export class ResourceCache {
private url: string;
/** 过期时间 */
private expireTime?: number;
/**
* @param url 资源路径
* @param expireTime 过期时间
*/
constructor(url: string, expireTime?: number | string) {
this.url = url;
let time: number | undefined;
if (typeof expireTime === 'string') {
const unit = (expireTime as string).slice(
-1,
) as keyof typeof Time;
time =
Number(Time[unit]) *
Number(expireTime.slice(0, -1));
} else {
time = expireTime;
}
this.expireTime = time;
}
private async fetch() {
try {
const response = await fetch(this.url);
const blob = await response.blob();
// 写入缓存
await setCache({
url: this.url,
content: blob,
expireTime: this.expireTime,
});
return blob;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
}
async get() {
try {
const cache = await getCache(this.url);
// 未击中缓存
if (!cache) {
return await this.fetch();
}
// 设置了过期时间
else if (this.expireTime) {
// 过期
if (
Date.now() - cache.timestamp >
this.expireTime
) {
return await this.fetch();
}
}
// 击中缓存切未过期
return cache.content;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
}
/**
* @description 清除缓存
*/
static async clear() {
try {
await clearCache();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
}
}
/**
* time to ms
*/
enum Time {
/** hour */
h = 60 * 60 * 1000,
/** day */
d = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
/** week */
w = 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
/** month */
m = 30 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
/** year */
y = 365 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
}一般的js-sdk更新频率很低且向下兼容,我们可以将它缓存再indexedDB中,当下次再次加载时,我们可以直接从缓存中获取,而不需要再次请求远端js-sdk
/**
* @description 加载远端js-sdk
* @param url 远端js脚本地址
* @param id 创建script标签的id
*/
export async function remoteJsToScript(
url: string,
id: string = 'fetch-script',
expireTime?: string | number,
) {
const script =
document.getElementById(id) ??
document.createElement('script');
script.id = id;
const cache = new ResourceCache(url, expireTime);
script.innerHTML =
(await (await cache.get())?.text()) ?? '';
document.body.appendChild(script);
}/**
* @description 调用迅雷下载
*/
export async function thunderDownload(
/** 指定任务组名称,可将批量任务合并成类似BT任务的【任务组】,迅雷将在下载目录中创建同名子文件夹保存所有下载文件。【推荐填写。若不填此项,迅雷下载列表会显示所有本次创建的下载任务,可能会使用户的下载列表显得杂乱】 */
taskGroupName: string,
tasks: {
url: string; // 指定下载地址【必填项】
/** 指定文件的下载目录,相对于当前的downloadDir目录【一般不必填写,除非某些文件的下载地址的路径不符合你的需求】 */
dir: string;
}[],
) {
await remoteJsToScript(
'//open.thunderurl.com/thunder-link.js',
'thunder',
'1m',
);
const thunderLink = (window as any).thunderLink;
thunderLink.newTask({
taskGroupName,
hideInfo: '1', // 是否隐藏下载任务信息
hideYunPan: '1', // 是否隐藏云盘
hideWin: '1', // 是否隐藏下载窗口
downloadDir:
taskGroupName.length === 1 ? '' : taskGroupName, // 指定当前任务的下载目录名称,迅雷会在用户剩余空间最大的磁盘根目录中创建这个目录。【若不填此项,会下载到用户默认下载目录】
tasks,
});
}效果图 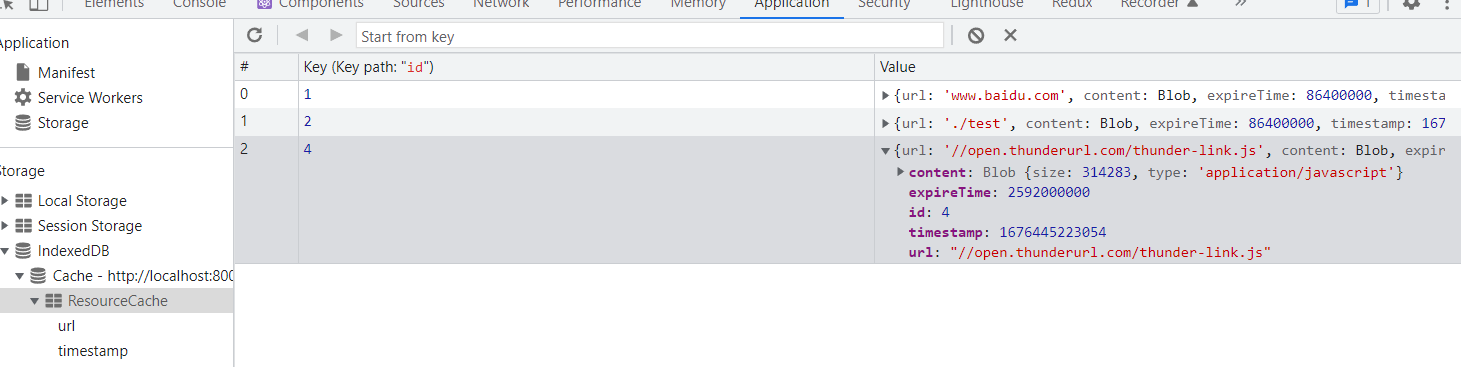 成功的将js以blob的形式存储在indexedDB中,当下次再次加载时,我们可以直接从缓存中获取。不仅是js,我们还可以缓存css、图片、3D模型、音频、视频等资源。
成功的将js以blob的形式存储在indexedDB中,当下次再次加载时,我们可以直接从缓存中获取。不仅是js,我们还可以缓存css、图片、3D模型、音频、视频等资源。
本文介绍了如何使用indexedDB来缓存资源,当下次再次加载时,我们可以直接从缓存中获取,而不需要再次请求远端资源,从而提升用户体验,减少请求次数,减少服务器压力,减少带宽消耗。